Enterprise data doesn't arrive in a single format. Customer interactions span text tickets, screenshots, recorded calls, and videos. Product knowledge lives in PDFs filled with diagrams and annotated images. Operational signals flow in as logs, metrics, and sensor outputs. When AI systems treat these as isolated data sources, they lose the ability to reason across real-world workflows and that's where things break down.
The impact shows up across industries. A customer support team loses resolution time when an agent can't connect a written complaint to the accompanying error screenshot and relevant documentation. A retailer struggles to deliver accurate product recommendations when images, videos, and descriptions live in separate, disconnected systems. An operations team misses critical signals when logs and sensor outputs can't be evaluated alongside incident reports. In each case, the problem isn't a lack of data, it's the inability to reason across it.
Multimodal compound AI systems solve this by processing and aligning text, image, audio, video, and structured data within a single execution context. Through shared representations, cross-modal retrieval, and coordinated reasoning, these systems handle the full complexity of how enterprise information actually exists.
Why Single-Modality Pipelines Fall Short
Consider a typical support workflow: a written issue description, a screenshot of an error state, and a reference to internal documentation. Process each input independently and you introduce ambiguity, increase error rates, and slow resolution times.
Multimodal systems eliminate this fragmentation. By jointly evaluating inputs across formats, they improve retrieval recall, reduce unnecessary follow-up queries, and produce higher-confidence outputs. In production, that means more reliable automation, better decision support, and lower operational overhead.
The Foundation: Multimodal Embeddings
At the core of any multimodal system is the construction and alignment of embeddings across modalities. Text, image, audio, and video are each transformed into vector representations that enable similarity search, retrieval, and downstream reasoning.
Each modality brings its own constraints:
- Text embeddings emphasize semantic relationships and compositional meaning.
- Image embeddings capture spatial structure and visual semantics.
- Audio and video embeddings must preserve temporal relationships.
- Structured data requires schema alignment and deterministic interpretation.
A production-grade system must manage modality-specific preprocessing, embedding drift, missing or partial inputs, and conflicting signals. Alignment errors at this layer propagate downstream making observability and validation non-negotiable.
How the System Works: Two Pipelines
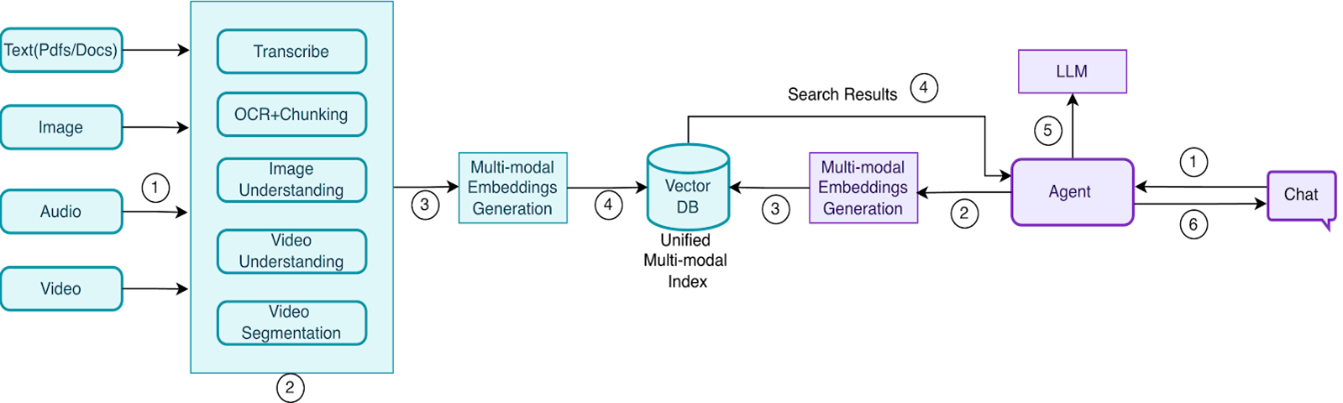
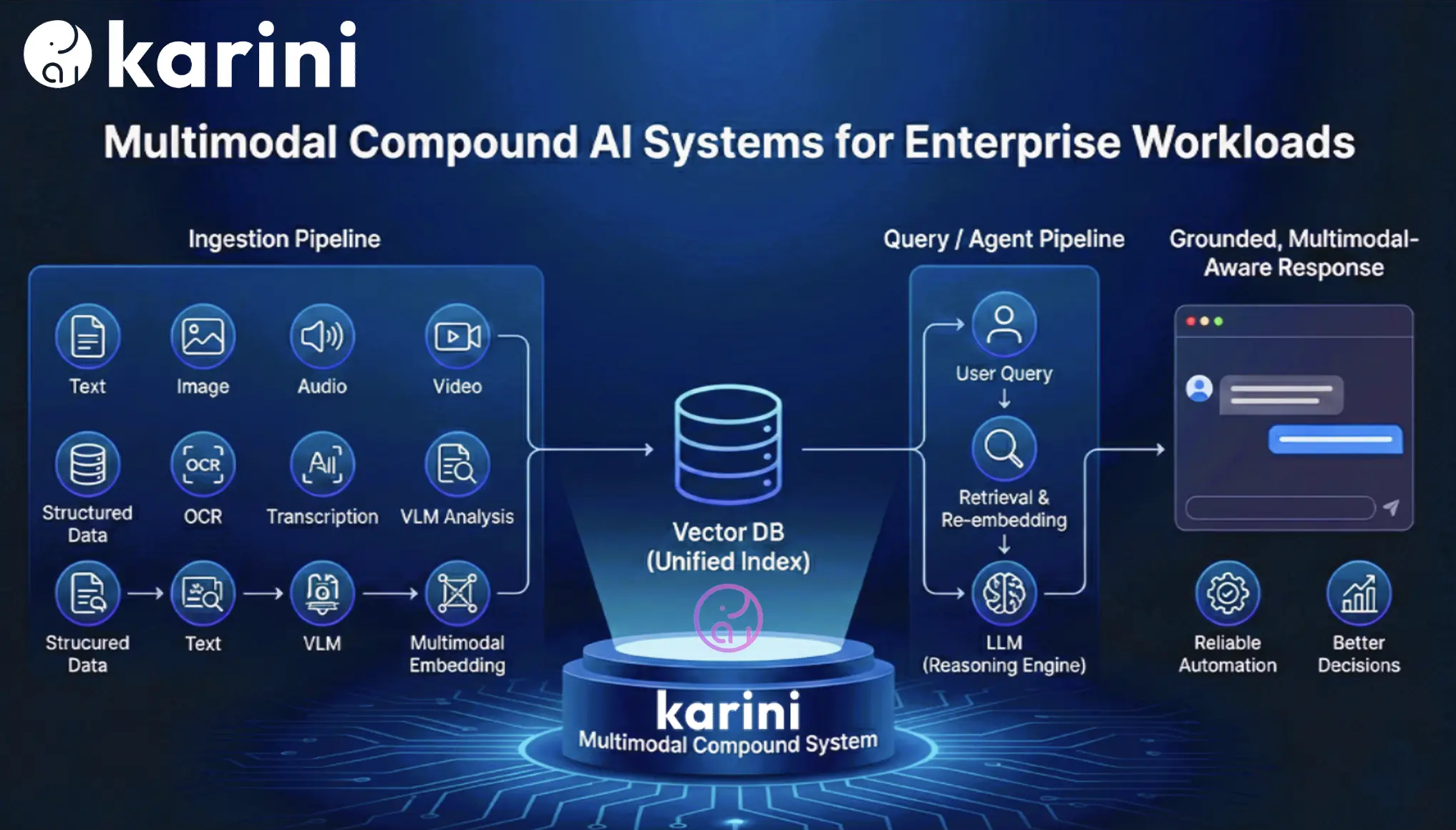
Ingestion Pipeline (Offline)
Raw content is ingested and routed by modality: audio is transcribed, text goes through OCR and chunking, images are summarized via vision models, and video is analyzed for both visual and audio content. The processed outputs are converted into dense vector embeddings and stored in a unified multimodal index within a Vector DB ready to be queried at runtime.
Query / Agent Pipeline (Online)
When a user submits a query, an agent retrieves the most relevant multimodal chunks from the Vector DB. Those results are re-embedded at query time to produce a context-aware representation, which is passed to an LLM. The model generates a grounded, multimodal-aware response that's delivered back to the user completing the loop.
Karini AI Multimodal Knowledgebase
Karini AI provides a purpose-built multimodal knowledgebase with capabilities across every stage of this pipeline:
-
Image Understanding: Process images using vision language models (VLMs) to generate rich, searchable textual descriptions. Supports configurable prompts and multiple VLM providers.
-
Audio Transcription & Understanding: Automatically transcribe audio using Amazon Transcribe or other providers, with intelligent segmentation (default 30-second chunks) and semantic search across spoken content.
-
Video Understanding & Analysis: Extract visual descriptions via VLMs at configurable intervals and transcribe audio tracks simultaneously, creating a rich, timestamped, searchable representation of every video segment.
-
Unified Multimodal Embeddings: Generate embeddings across all modalities using Amazon Nova's multimodal embedding model, creating a single vector space where users can search across content types seamlessly.
-
Intelligent Segmentation & Chunking: Automatically segment long-form audio and video into manageable chunks while maintaining context, merging transcriptions up to 512 tokens before embedding for optimal retrieval quality and cost efficiency.
-
Flexible Processing Pipelines: Enable or disable image understanding, audio transcription, or video analysis independently. Each pipeline supports multiple processing methods with customizable configurations.
-
Rich Metadata Preservation: Retain temporal information, source references, processing methods, and custom metadata throughout — enabling precise filtering, temporal queries, and compliance audit trails.
-
Scalable, Distributed Processing: Process large multimodal datasets using Ray for distributed computing, with automatic retry logic, resource management, and parallel execution across workers.
-
Cost-Optimized Embedding: Generate embeddings only for meaningful content (descriptions, transcriptions, summaries) rather than raw media files, with support for both synchronous and asynchronous invocation.
-
Comprehensive Processing Reports: Get full visibility into pipeline performance through detailed HTML reports covering embedding counts by modality, success rates, and cost breakdowns.
From Data to Working Chat Assistant in 30 Minutes
To make this concrete, consider a retailer with a large catalog of product images, videos, and descriptions who wants to build an agentic self-service discovery and recommendation assistant. Here's how to go from raw data to a fully deployed chat assistant using Karini:
- Build a Multimodal Knowledgebase: Ingest and index your product content across all modalities.

- Build and Test Your Agent: Connect the knowledgebase to an agent and validate retrieval and reasoning.

- Build the Agentic Workflow: Orchestrate the end-to-end interaction logic.
- Test the Chat Assistant: Run the full experience and prepare for deployment.
Conclusion
Enterprise AI systems need to reflect the multimodal reality of how businesses actually operate. Multimodal compound AI systems enable shared context across documents, images, audio, video, and structured data improving both retrieval accuracy and downstream reasoning quality.
But powerful models alone aren't enough. Success depends on careful system design, clear modality boundaries, reliable orchestration, and end-to-end observability.
Karini provides the infrastructure to build, deploy, and operate multimodal compound AI systems at enterprise scale.